Many think of GIS (geographic information systems) as just a way to “make maps.” However, the definition of a “map” has changed immensely since the printed road map – a series of lines that simply displays the roads and routes of a particular city or state. Today’s technologies allow us to move far beyond the static map and organize data based on time and place. The result? Creating maps that evolve along with the spaces they’re designed for. This is especially helpful when communities are planning for future growth. Will municipal infrastructure support an influx in population? How soon and where do new systems or upgrades need to be made? There is an efficient and effective means to find the answers to such questions. Welcome to the world of geospatial analysis.
What is geospatial analysis?
Geospatial analysis uses statistical techniques on data that has a location associated with it. Statistics are often compiled in a spreadsheet with the output appearing as a table or a chart. However, when you add a geographic component to that data, it becomes possible to map the outputs and draw new insights. This “map” is composed of geospatial data. It helps users better visualize trends and more effectively communicate those findings with others. Geospatial data can be a powerful tool to drive smart decision making and long-term planning.
Geospatial analysis for public works
GIS and geospatial analysis play an important role in engineering planning and design projects, helping municipalities of all sizes plan and prepare for future growth.
Many communities are growing quickly, and public works departments need to ensure that their existing infrastructure can handle the growing population. Let’s say, for example, that a city is looking to add a new housing development. Do the existing sanitary mains have enough capacity to support a new subdivision? Can gravity mains connect to the system or will a new lift station be necessary to reach the wastewater treatment plant?
GIS professionals work in tandem with engineers and planners to tackle these types of questions quickly and efficiently. This is done by utilizing geospatial analysis to generate a variety of map layers that evaluate the proposed future development area and how and where utilities might connect.
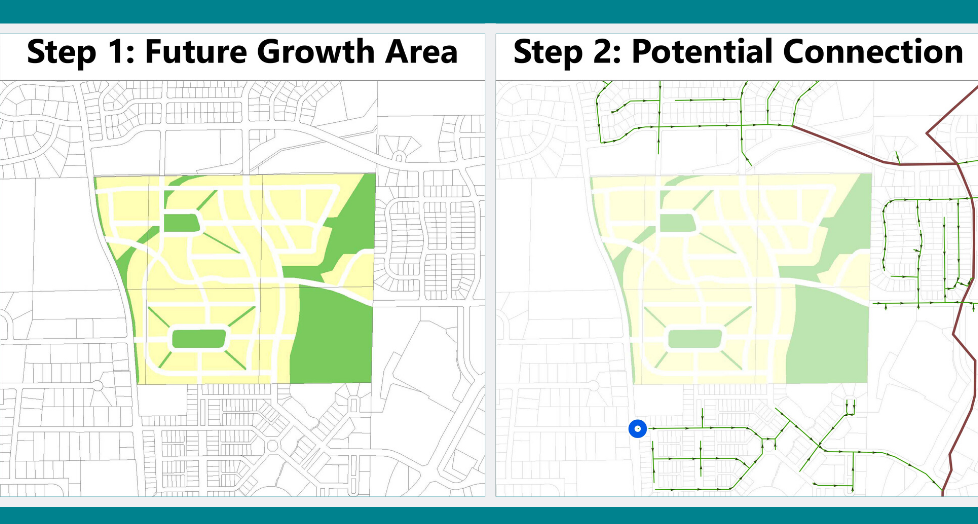
Step 1: Identify the proposed growth area by referencing existing comprehensive plans and coordinating with city planners.
Step 2: Leverage mapped utility infrastructure to identify potential connection points to service the new development.
Step 3: Identify any potential development limitations (e.g. wetlands, wildlife habitat, etc.) that should be protected or preserved.
Step 4: Leverage LiDAR elevation data which will dictate the ability to bury new utility lines safety underground.
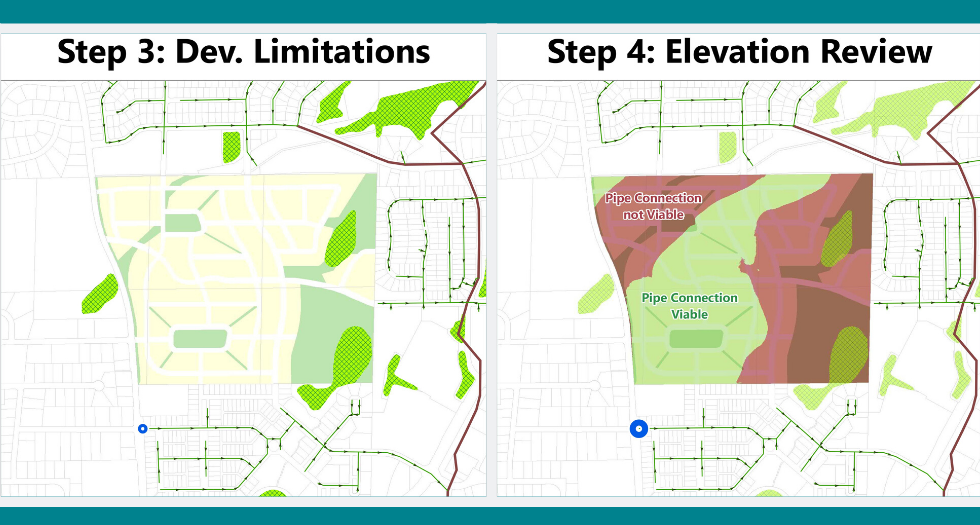
Using automation tools, this process can be repeated as often as needed, and can be adjusted in real time in order to make alterations or test a variety of scenarios. The mapped outputs allow for clients to better visualize their growth options, understand the existing limitations and most successfully plan for the future.
Geospatial analysis is an innovative and cost-effective way for communities to most accurately prepare for all the exciting opportunities and changes that lie ahead. Whether applied to utility infrastructure needs, prioritizing road intersections for safety improvements, finding the best spot for a new housing development or siting a new community park, geospatial analysis is proving that foresight — not hindsight — is 20/20.
Start a conversation today about how MSA can develop new geospatial analysis solutions for your community’s needs.
